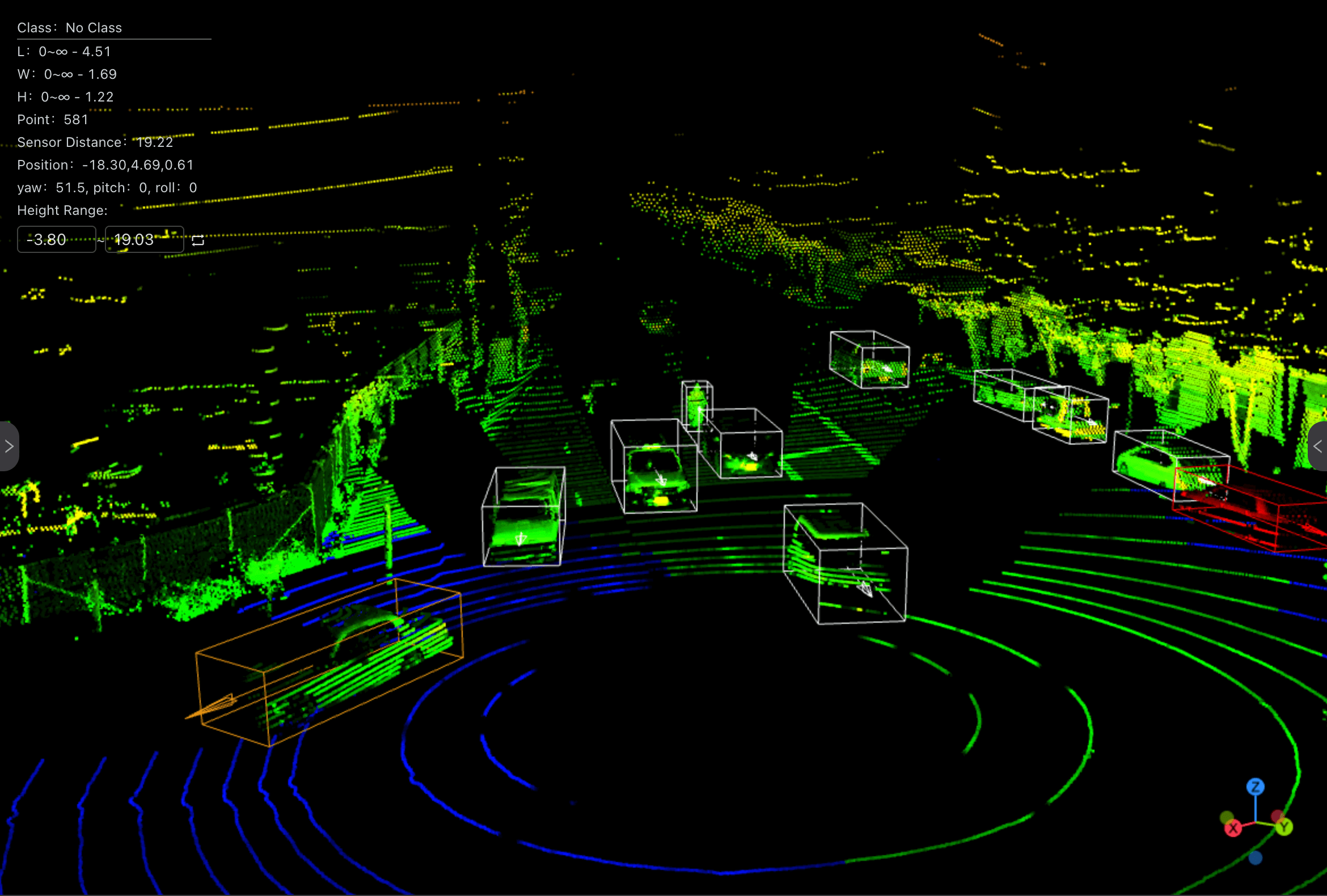
Introduction
3D bounding box (3D Bbox) annotation is a fundamental task to train autonomous driving models. It enables AI models to accurately detect, track, and classify objects in LiDAR point clouds and multi-sensor fusion datasets. However, the efficiency and accuracy of the annotation process heavily depend on the annotation tool used.
Choosing the right 3D annotation tool can significantly impact the labeling quality, project speed, and cost-effectiveness. In this article, we will do a quick comparison of two popular tools, BasicAI and CVAT, to help you make an informed decision based on your project’s complexity and scale.
Key Differences Between BasicAI and CVAT for 3D Bbox Annotation
1- Visualization
The quality of 3D annotation is highly dependent on the visualization options offered by the tool used. Good visualization enables annotators to interact effectively with point clouds, improve annotation accuracy and better distinguish complex objects. Good 3D annotation tools make it easy to combine and change visualization types (e.g., with respect to distance, elevation and intensity) to facilitate annotation.
- CVAT : No Point Intensity Visualization – CVAT does not display the intensity of LiDAR points, making it harder to differentiate objects in the dataset. This is a crucial feature for applications such as autonomous driving, where intensity helps distinguish between road surfaces, pedestrians, and vehicles. It’s especially useful for highly reflective objects like metal signs, which can create artifacts. Using intensity helps distinguish artifacts from the actual object.
- BasicAI : Customizable Visualization – Annotators can highlight specific object features, such as height, distance, or point intensity, to better understand the LiDAR Point cloud, refine annotations and improve labeling precision.
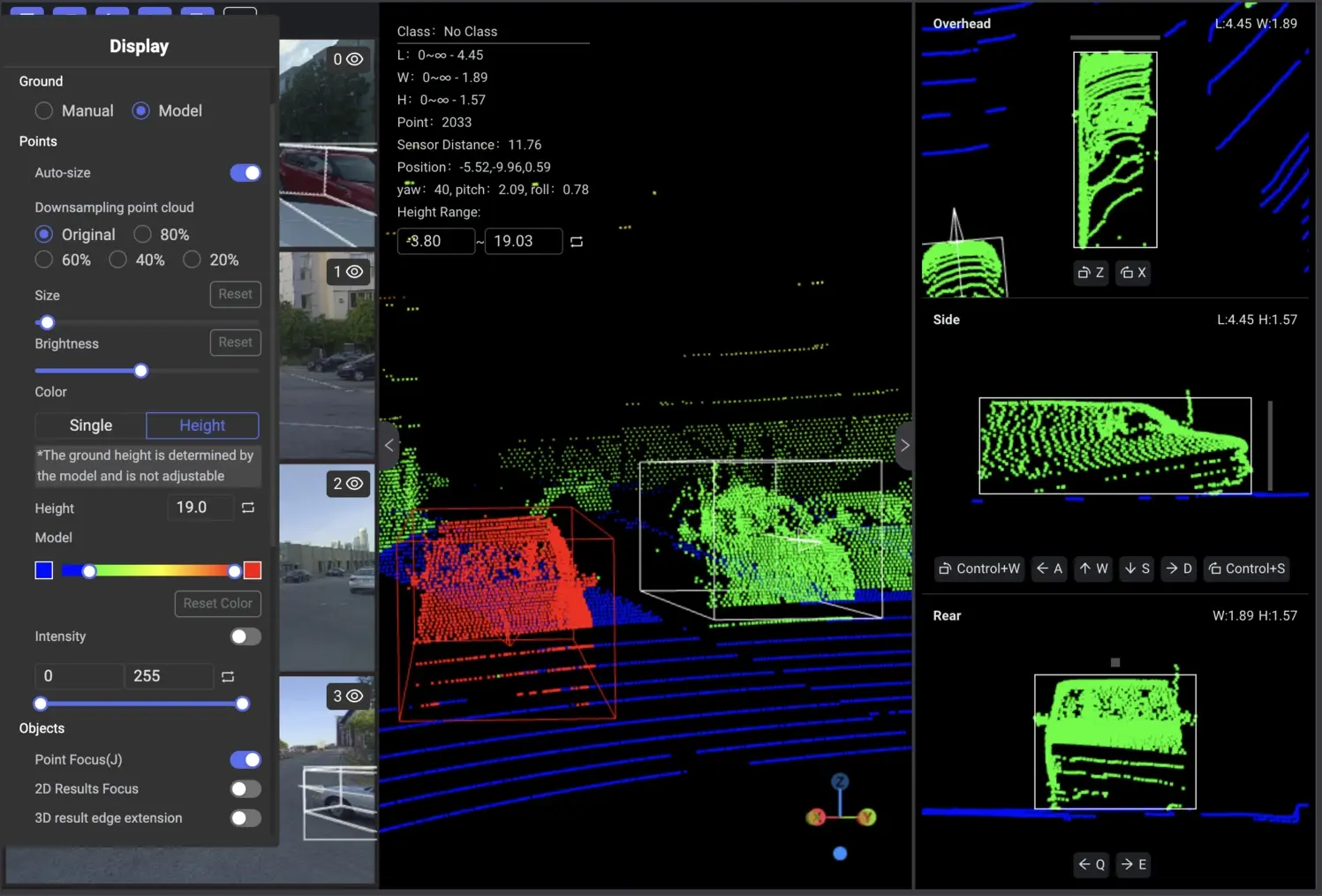
While CVAT is a widely used open-source annotation tool, it lacks critical features for 3D LiDAR annotation. These limitations can slow down the annotation process and impact labeling precision. BasicAI enhances annotation efficiency with AI-powered tools that automate and optimize the 3D bounding box labeling process.
2- AI Assisted annotation
- CVAT : No AI-Assisted 3D Bbox Creation – In CVAT, bounding boxes are not easy to position at the creation step and must be manually adjusted from a basic cubic shape, leading to strong inefficiencies for the labelers. Labelers must manually translate, rotate, and resize the box from a basic cubic shape, which can significantly increase labeling time.
- BasicAI : Smart 3D Bbox Generation – BasicAI’s AI-assisted tool generates an initial 3D bounding box based on an initial 2D Bbox drawn by the labeler which is usually well centered on the actual 3D object. This dramatically reduces annotation time, unlike CVAT, where annotators must create each box from scratch.
3- Editing & Refinement Capabilities
Annotation tools should allow seamless modifications to improve labeling accuracy. BasicAI offers a more intuitive and precise editing experience than CVAT.
- BasicAI enables precise rotation and translation of 3D bounding boxes using discrete angle and translation values with dedicated buttons, making adjustments fast and intuitive. Unlike CVAT, where manual rotation and translation rely on the mouse cursor—often leading to frustrating and unstable edits—BasicAI’s streamlined tools allow annotators to modify Bboxes efficiently without wasting time searching for the correct transformation points.
4. Interpolation & Extrapolation
Interpolation and extrapolation are key automation features that reduce manual effort in time-series annotation (e.g., video frames, LiDAR sequences).
Limited Interpolation in CVAT
- CVAT only allows forward interpolation, meaning annotations cannot be propagated backward across frames.
- CVAT also lacks AI-driven extrapolation, requiring annotators more work to manually adjust bounding boxes over time.
Enhanced Interpolation & AI-Powered Extrapolation in BasicAI
- Two-Way Interpolation – BasicAI supports both forward and backward interpolation, making it more efficient for moving objects in autonomous driving datasets. This is very important as 3D cuboid is easier to create when you best see the object and estimate its size and then extrapolate backward and forward from there.
- AI-Powered Extrapolation – BasciAI tool can predict bounding box positions beyond current labeled frames, by using an AI model to track the object dynamically, significantly reducing the time per 3D Bbox.
📌 The best use case for BasicAI’s Two-way interpolation feature is, while labeling autonomous driving datasets, the easiest moment for creating precise 3D Bboxes is often when a vehicle is closest to the LiDAR sensor. With BasicAI, annotators can set a reference Bbox at this optimal point and interpolate both forward and backward, maximizing accuracy and saving time.
Conclusion
Choosing the right 3D annotation tool depends on your project complexity, scale, and efficiency needs.
- CVAT is a solid open-source tool for basic 3D Bbox annotation and a smaller amount of frames. However, it lacks AI-powered automation, intuitive editing, and advanced interpolation/extrapolation features to make it really usable for larger Lidar fusion projects.
- BasicAI, designed for data fusion and LiDAR annotation, offers AI-assisted 3D bounding box creation, seamless editing, and advanced interpolation/extrapolation. These features make it the preferred tool for high-precision, large-scale annotation projects.
All these factors led us to start a data fusion and LiDAR annotation project on CVAT but ultimately migrate to BasicAI for its improved efficiency.
🔎 Need high-quality 3D annotations? People for AI provides expert data annotation services using BasicAI and other industry-leading tools. Contact us today to optimize your LiDAR, video, and image annotation workflows. 🚀
📩 Get in touch with our team at People for AI